(Up-to-date source of this post.)
Cellular network
- a radio network distributed over land areas called cells
- each cell is served by at least one transceiver - BTS (Base Transceiver Station) = cell site
- this enables a large number of portable transceivers (e.g. mobile phones) to communicate with each other
- example of a cellular network: the mobile phone network or PLMN
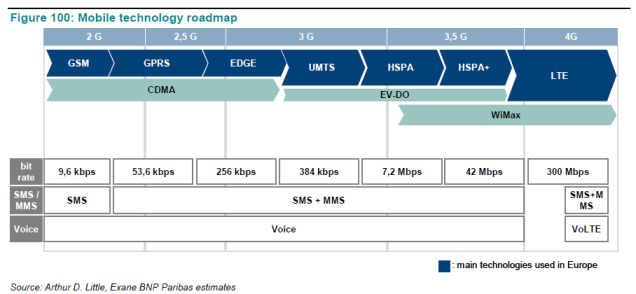
GSM
- World's most popular standard for mobile telephony systems (80% of mobile market uses the standard)
- both signaling and speech channels are digital (1G was analog, ex. NMT)
- second generation (2G) of mobile phone system
- GSM release '97 - added packet data capabilities via GPRS
- GSM release '99 - higher data transmission via EDGE
- UMTS (Universal Mobile Telecommunications System) - 3G mobile cellular technology for networks based on GSM standards
- LTE - 4G, standard for wireless communication of high-speed data for mobile phones and data terminals, based on the GSM/EDGE and UMTS/HSPA
Network Structure
GSM PLMN has two main logical domains:
- access network - most used access networks in western Europe as of 2009 (can be deployed in parallel):
- GERAN (GSM EDGE radio access network)
- UTRAN (UMTS terrestrial radio access network) - HSPA can be implemented into UMTS to increase data transfer speed
- core network
- circuit switched domain
- packet switched domain
- IP multimedia subsystem (IMS)
GPRS/UMTS architecture with the main interfaces:

The network is structured into a number of discrete sections:
- the base station subsystem (BSS) - handles traffic and signaling between a mobile phone and the NSS (access network)
- the network and switching subsystem (NSS) - part of the network most similar to a fixed network (VOICE, circuit switched)
- the GPRS core network - optional part for packet based Internet connections (NON-VOICE, packet switched)
- operations support system (OSS) for maintenance

See this picture for GSM communication.
BSC = Base Station Controller
- intelligence behind the BTSs (allocation of radio channels, measurements from the mobile phones, handover control from BTS to BTS)
- concentrator towards the mobile switching center (MSC)
- the most robust element in the BSS
- often based on a distributed computer architecture
PCU = Packet Control Unit
- late addition to the GSM standard
- processing tasks for packet data
MSC = Mobile Switching Centre
HLR = Home Location Register
- database of subscribers
- a central database that contains details of each mobile phone subscriber that is authorized to use the GSM and/or WCDMA core network of this PLMN
VLR = Visitor Location Register
- register of roaming subscribers
AUC
- database of authentication keys
EIR
- stolen devices (phones) register
SS7 = Signaling System #7
- a set of telephone signaling protocols
- main purpose: setup/tear down telephone calls
- other uses: number portability, SMS, etc.
SGSN = Serving GPRS Support Node
- delivery of data packets from and to mobile stations withing its geographical service area
- packet routing and transfer, mobility management, logical link management, authentication and charging functions
GGSN = Gateway GPRS Support Node
- main component of the GPRS network
- inter-networking between the GPRS network and external packet switched networks
- router to a sub-network
AT commands
Huawei, Android
at+cgmi- manufacturerat+cgmm- modelat+cimi- IMSIat+cmgw="0914123456",145,"STO UNSENT"- store message to memoryat+cmgl="all"- show stored messagesat+cmss=3- send message n. 3 from memoryat+cmgd=2- delete message n. 2 from memory
Links
General
- Mobile Internet Usage -- Thesis by a Finnish student
- Mobile network
- P. Luptak: Strucny prehlad do bezpecnosti GSM (in Slovak)
AT commands
- Send SMS using AT commands - I was able to send an SMS following this guide
- AT+C commands of GSM devices
- http://www.traud.de/gsm/
- SMS Tutorial
Hacking
- Osmocom OpenBSC - functionality of BSC (Base Station Controller), MSC (Mobile Switching Center), HLR (Home Location Register), AuC (Authentication Center), VLR (Visitor Location Register), EIR (Equipment Identity Register)
- AirProbe - GSM-Sniffer
- Kraken - cryptographic weaknesses found in today's cellular networks
- Nové trendy v GSM odpočúvaní (P. Luptak)
- GSM security map
- Decrypting GSM phone calls - tools
- 28c3: Defending mobile phones (Video) - impersonating another MS
- 27c3: Wideband GSM Sniffing (Video) -- Call/SMS interception and decrypting
- clarifications about 27C3 GSM Sniff Talk -- you can't get the tools used for cracking A5/1 and traffic sniffing
PDUSpy
Books
- M. Grayson et al.: IP Design for Mobile Networks (Cisco Press, 2009)
- A. Henry-Labordere, V. Jonack: SMS and MMS Interworking in Mobile Networks (Artech House, 2004)
No comments:
Post a Comment